This tutorial deals with Fusion Payroll, and how it functions.
Having dealt with an Overview of Oracle Fusion and the Functional Setup Manager (FSM), we will now look at Common Application Configuration.
The topics covered in this first part of the tutorial are:
● Initial Setup
● Synchronisation of Users and Roles
● Implementation Users Setup
● Geographies
● Currencies
● Enterprise - An Overview
Initial Setup
Any user or goal definition comes under Oracle Identity Management (OIM). It maintains Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) user accounts for users of Oracle. OIM also stores the definitions of abstract, job, and data roles and holds information about roles that are provisioned to users.
It can be a non-cloud or a cloud implementation, and each of them have their own super user. The FA Admin Superuser is for non-cloud implementation, while Oracle Cloud Administration User is for cloud implementation.
First, sign into Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) as the OIM Administration user, and provision the IT Security Manager job role with roles for user and role management. This enables the superuser account, which is provisioned with the IT Security Manager role to create implementation users. Then, the offering to be implemented has to be selected and finally, the setup tasks needed to implement the offering are generated.
The flowchart below depicts the role-assigning process clearly.
Synchronisation of Users and Roles
Existing information and any changes to users, their roles, and the roles provisioned to users must be copied from the LDAP directory to the Oracle Fusion Application tables. To copy this information, use the task Run User and Roles Synchronization Process. This task calls the Retrieve Latest LDAP Changes process.
Implementation Users Setup
The implementation users perform tasks in implementation projects. There are a number of tasks related to implementation users:
● Create Implementation Users:
○ At least one implementation user is required.
○ Multiple users are recommended to ensure segregation of critical duties.
● Create Data Role for Implementation Users:
○ Data Roles are assigned so that the implementation users can access appropriate data depending upon their tasks.
○ If the Oracle Workforce Compensation Cloud service is licensed, you can create HCM data roles to provide access to compensation setup data.
● Provision Roles to Implementation Users:
○ Predefined job and abstract roles are assigned (e.g. Application Implementation Consultant, Application Implementation Manager, HR Specialist, Payroll Manager, etc.).
○ The newly created Data Roles are also assigned.
Geographies
Geographies are a mechanism through which you can create geography structures defined for localisation and legislations. The task associated with geographies is Manage Geographies.
Geography Structure
A geography structure defines the geography for each country. It defines which geography types are part of the country structure and how they are hierarchically related within the structure.
Geography Types
Geography types typically include State, City, and Postal Code. State is the highest geography level within the country. City and Postal Code follow, with Postal Code being the lowest level within the country structure. Geography Hierarchy
Once the structure is created, the geography hierarchy has to be defined. Geography Hierarchy is a data model that creates conceptual parent-child relationships between geographies. The top level of the hierarchy is country (parent). The hierarchy contains several child geographies.
Geography Validation
Geography validation determines the geography mapping and validation for a country’s address styles, as well as the overall validation control for a country. The default address style format for a country is taken.
By defining the mapping and validation for this format, you ensure that validations can be performed for any address in the country. You can enable a list of values for tax validation or geography validation.
Currencies
Currencies are extensively used in financials. You can manage currencies and their attributes, including Currency Codes, Date Ranges, and Symbols. Euro Currency Deviation is used in conversion and derivation of European currencies in the European Union.
You can also manage Conversion Rates. Conversion rate types are used to automatically assign a rate when accounting functions are performed. This will determine how the currency conversion is done.
For example, you can set the conversion rate for converting Pounds to Dollars, Dollars to Euros, etc. There are four Seed Conversion Rate types - Spot, Corporate, User, and Fixed Daily Rates.
Enterprise - An Overview
The enterprise is the top-level organisation, which acts as an umbrella for all data in the implementation. There can only be one enterprise per instance. For example, if a company has operations in more than one country, there is one enterprise. This enterprise will encompass the whole of the company’s operations in all countries, with each country’s operation having its specific legislation attached to it.
The implementation is affected by the following:
● Industry
● Business unit requirements for autonomy
● Business and accounting policies
● Business functions performed by business units (optionally, those that are centralised in shared service centres)
● Locations of facilities
There are three fundamental structures for an enterprise: legal (depending on the country’s location), managerial (for managing the hierarchy), and functional (for the activities undergone).
Legal Structure
The legal structure is defined by a legal entity. It is a legal system which specifies the rules and regulations to be followed when buying and selling, owning, and employing within a jurisdiction. It is specific to the legislation or legal system.
The legal system has to be understood thoroughly before registering the entity. A legally recognised entity can own and trade assets, as well as employ people within the jurisdiction it is in. Once the organisation is registered, there are certain responsibilities pertaining to its legal system.
Management Structure
This structure is concerned with the hierarchy within the management, its objectives, and how they are to be achieved. This is done through divisions and business units.
The enterprise is segregated by its strategic objectives and measurements of their results. Functional Structure This structure is based on the functions within the organisations. Based on these functions, appropriate departments are formed.
The functional structure is structured around people and their competencies after dividing them into specific teams like Sales, Manufacturing, and Service. The organisation must manage and report revenues, cost of sales, and functional expenses.
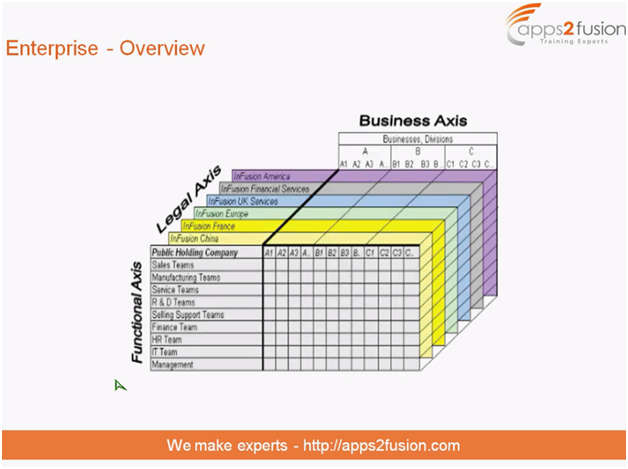
Fig. 2 - The axial view of an enterprise
<-->