SAP ERP provides its customers with various modules to cater their business requirements. SAP Finance, being one of the highly integrated modules, runs through all the other modules. To Map the system with our business requirement firstly we need to understand the definition of the SAP FI organizational Structure and its overall usage and purpose. After understanding the same we can be in a position to decide which of the organizational hierarchy units do we need to use and which we don't.
Client:
The client is the highest level in the SAP ERP System hierarchy. Specifications of the data that is valid for all the organizational units are entered at client level. This helps in reducing the entry of information more than once, which can be utilized as for all the modules as common. Each Client is a technically independent unit with a separate master records and a complete set of tables and data. In business terms a client level often corresponds to that of a corporate group or group of affiliated companies.
If we compare the SAP Organizational Hierarchy with Oracle EBS, the client in SAP is equivalent to the production server in Oracle EBS. While implementing Oracle EBS, we configure various instances like CRP1, CRP2, UAT, Test, and Production instance. Each environment or instance is independent from the other; has its separate master records and its own set of tables.
Company Code:
Company code represents an independent balancing/legal accounting entity. Financial statements required by law can be created at company code level. Therefore a company code is the minimum structure necessary in SAP ERP Financials. Every organization for which a financial statement and profit and loss statement P & L is to be created must be stored as a company code in the system. It is the most important organizational unit as it is the minimum for other modules also. Assignments of other modules organizational structure hierarchy (for example, MM, CO, PP, SD, and so on.) falls under the Company Code to provide the Inter module integration.
Company Code in SAP ERP is similar to an operating unit in Oracle EBS. Company code is used to segregate data in SAP from one user to another. We give access to users at company code level in SAP. It is quite similar to an operating unit, as we segregate the data in sub-ledgers at operating unit level. However in Oracle EBS we do not create P/L and balance sheet at OU level.
Business Area:
Business Area represents separate areas of operation within an organization and can be used across company codes. They are balancing entities that can create their own set of financial statements for internal or external purposes. It is therefore possible to save and evaluate transaction figures for each business area.
NOTE: With ECC 6.0 the usage of Business area has majorly been taken care of by Profit Centers. (A Functionality provided by SAP called document drilldown helps in creating Balance sheet at Business Area Level also)
Business area in SAP ERP is quite similar to a balancing segment value in Oracle EBS multi-org setup. Balancing segment is used to identify a company for which the financial statements are prepared. We can have multiple balancing segment values attached to a legal entity.
Profit center:
The profit center evaluates the success of individual independent areas within a company. These areas are responsible for costs and revenue. The aim of profit center invoice is to provide an internal analysis of profits. From an accounting point of view it must be determined whether only a profit and loss statement at profit center level is to be created or whether a financial statement is also to be created.(If a Balance sheet is required, like the business area the Document splitting functionality needs to be activated on Profit center level.)
We can prepare multiple segments in Oracle EBS in our Chart of accounts like Primary balancing segment, cost center, natural account, and secondary tracking segment. Profit center in SAP is equivalent to cost center in Oracle EBS. A Cost center is the segment for which costs are collected and reported.
Company:
Companies are used as a basis for the consolidation functions for financial accounting in the SAP system. A company can contain one or more company codes. The usage of these is part of preparations for consolidation.
The use of these organizational units prominently depends on the requirements of the customer’s internal and external accounting. Unlike Company codes all the other objects are optional.
Company in SAP ERP is quite similar to Legal entity in EBS multi-org setup. Though, in SAP it is not mandatory to define a company but in Oracle it is mandatory to define a company. We create the financial statements at company level in oracle EBS. Whichever organization has a separate legal registration or is a separate legal entity we consider it as a Legal entity in Oracle. A LE has implications of filing and paying taxes and producing financial statements.
Segment:
According to international accounting principles (IFRS 8 and SFAS 131) companies are obliged to provide information in their reports on the financial results of business segments (Operating elements). This is conducted using a Management Approach, which requires that segment information from internal reporting is constructed in the same way that the information is used to make decision on the allocation of resources to segments and evaluate performance.
Functional Area:
In cost of Sales accounting operating costs are sorted according to function (Administration, sales and so on.)
Note : The system derives the segments from profit centers.
How to determine the Organizational Structure of a Business unit:
We can use all the elements to have a slice through analysis or can use the minimum to keep the reporting at minimal and the derivation systematically.
So it is advisable to map the organizations structure appropriately and with utmost care taking into consideration the complexities of the business environment. Its internal reporting and external reporting ,legal obligation, analysis, profitability evaluation, cost analysis and management. The following quick questions can help you decide on your system organizational structure mapping.
- What is the most important accounting principle in my enterprise or corporate group.
- According to which accounting principles are figures reported internally/externally in my company.
- Does my company structure its profit and loss statement according to totals cost?
- Is my enterprise obliged to issue segment reporting according to the law
- Does my company have to issue a consolidated financial statement?
This step in preparing a company’s organizational Structure is of utmost importance.
To understand the mapping of the real time business enterprise lets take two examples to make the hierarchy clear.
Company 1 : XYZ Ltd
Company XYZ is a medium size company into Steel Business with its scope within India. They provide products as below Plates, Rods, and Pipes. They have to submit their books of accounts to the government on a yearly basis as per the Indian Accounting Standard. But also the company’s owners requires seeing the profitability of their business at their product level and on an overall company level.
How will the organizational hierarchy look like with the above scenario?
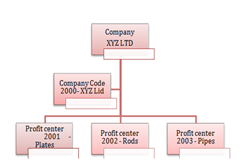 <-->
<-->
Company 2: ABC Ltd is a big multinational Company and it scope of work diversifies in various different field.
- ABC Pharmaceutical - India
ABC Retail
ABC Depots
ABC SEZ
- ABC Pharmaceutical – USA
ABC Retail
ABC Depots
- ABC Real Estate
The company wants to see it profitability sector wise instead on a product in the below case if the company required product level reporting as we could have created segments of its product line like. We can also create business areas of the same. To have a product wise Profitability analysis.
- Anti-Allergy
Cold and Cough medicines
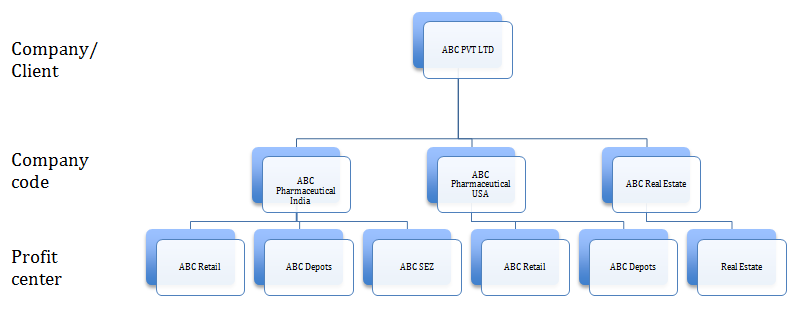 <-->
<-->
Therefore in the above scenario, there can exist various combinations of the usage of the organizational units to derive maximum benefits in SAP.












